After reading this post you will learn the following:-
- Introduction
- Etiology
- Clinical Features
- Histopathologic Features
- Clinical Significance
- Treatment
Introduction
Leukoedema Is Generalized Opacification Of Buccal Mucosa That Is Regarded As A Variation Of Normal. It Clinically Resembles Early Leukoplakia. It Is Considered To Be Variation Of Normal Rather Than A Disease because :
- It Can Be Identified In Majority Of Population
- Also, similar mucosa seen in the vagina & larynx
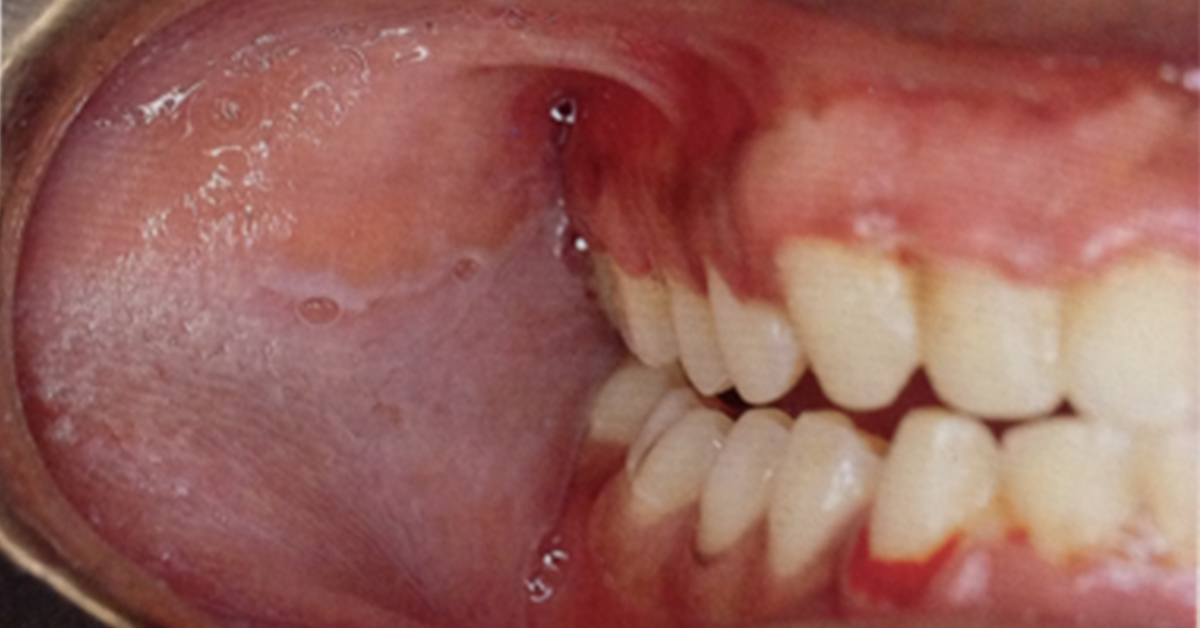
Leukoedema On Buccal Mucosa
Etiology
- To Date, Cause Has Not Been Established:-Smoking, Chewing Tobacco, Alcohol Ingestion, Bacterial Infection, Salivary Condition and Electrochemical Interactions
- None Of The Above Are Proven Cause
Clinical Features
- Usually discovered as incidental finding
- Asymptomatic
- More common in Blacks than in Whites, suggesting ethnic predisposition
- Appear as gray-white, diffuse, filmy, or milky surface
- More exaggerated cases show surface textural changes like wrinkling or corrugations
- In majority of cases, it occurs bilaterally and frequently involves most of the buccal mucosa and may extend forward onto the labial mucosa
- Most noticeable along the occlusal line in the bicuspid and molar region
- Do not rub off
- Leukoedema can be diagnosed clinically because the white appearance greatly diminishes or disappears when the cheek is stretched. This helps to distinguish it from other common white lesions, such as leukoplakia, candidiasis, & lichen planus
Histopathologic Features
- Increase In Thickness Of Epithelium
- Intracellular Edema Of Spinous Layer. These Cells Appear Extremely Large & Pale
- In Reticular Fashion, Cytoplasm-lost; Nuclei Absent/Clear/Pyknotic
- Superficial Parakeratosis
- Broad Rete Ridges- Irregularly Elongated
- Inflammatory Infiltrate In Connective Tissue Not Common Finding
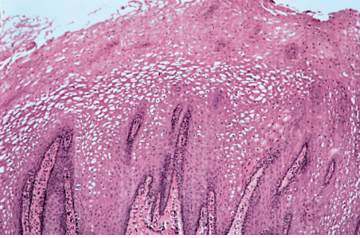 Leukoedema Histopathology
Leukoedema Histopathology Clinical Significance
- Leukoplakia Is More Apt To Develop In Leukoedema Than In Normal Epithelium
Treatment
- No Treatment Needed Since, No Malignant Potential
- If There Is Doubt In Diagnosis, Biopsy Can Be Performed
References
- Shafer’s Textbook Of Oral Pathology
- Neville Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, Fourth Edition –


