Outline
After reading this post you will learn the following about Squamous Papilloma :-
- Introduction & Etiology
- Clinical Features
- Histopathologic Features
- Treatment & Prognosis
Introduction
- Squamous papilloma is the fourth most common oral mucosal mass
- Associated with papillomavirus (HPV); commonly caused by HPV types 6 and 11
- Although all HPV lesions are infective, squamous papilloma has low virulence and infectivity, and is not very contagious
- Clinically and microscopically indistinguishable from verruca vulgaris (common wart), which is a virus-induced focal papillary hyperplasia of the epidermis
Clinical Features
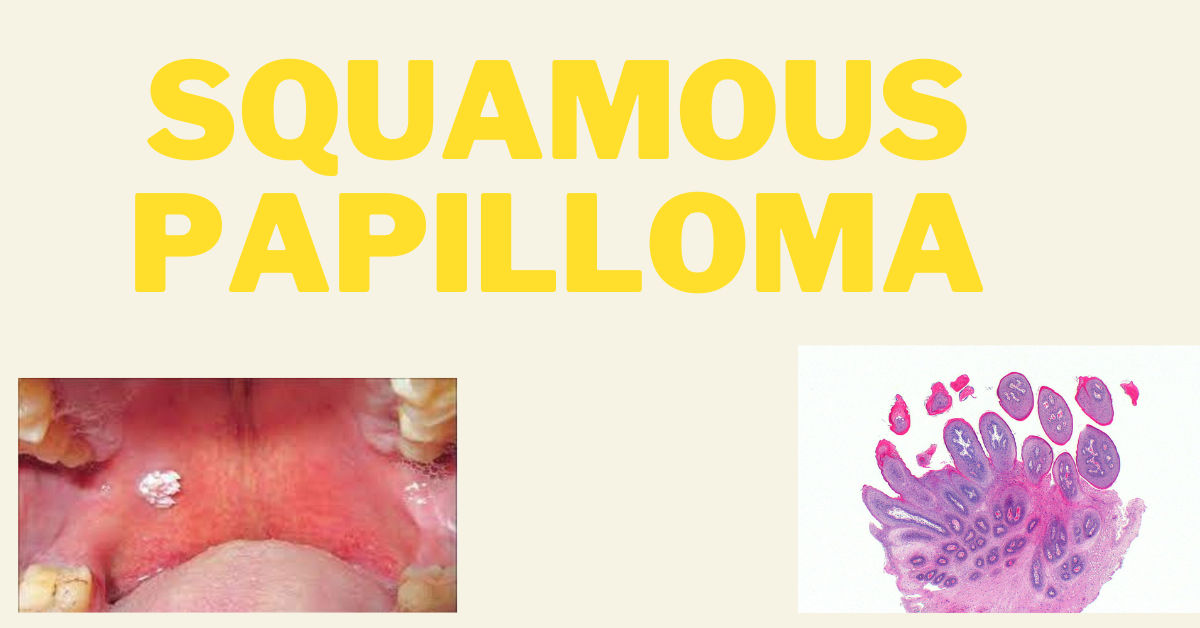
- Exophytic growth with numerous small finger-like projections, resulting in a roughened, verrucous, or ‘cauliflower-like’ surface
- Nearly always a well-circumscribed pedunculated tumor, occasionally sessile
- Painless; usually white but sometimes pink in color
- Common intraoral sites include tongue, lips, buccal mucosa, gingiva, and palate, particularly near the uvula
- Majority are small, measuring a few millimeters in diameter, but can reach several centimeters
- Occur at any age, including young children
COMMON WART/VERRUCA VULGARIS:
- Frequent tumor of the skin, analogous to oral papilloma
- Uncommon on oral mucous membranes but extremely common on the skin
- Associated viruses include HPV-2, HPV-4, and HPV-40
- Clinically similar to oral papilloma; contagious and capable of spreading via autoinoculation
Cowden’s Syndrome:
- Papilloma-like or papillomatous lesions, as well as ‘pebbly’ lesions and fibromas, are recognized as manifestations of this syndrome in the oral cavity
Histopathologic Features :-
- Consists of many long, thin, finger-like projections extending above the surface of the mucosa
- Each projection is made up of a continuous layer of stratified squamous epithelium with a central connective tissue core supporting nutrient blood vessels
- Some papillomas exhibit hyperkeratosis, likely due to location and frictional irritation
- Essential feature is a proliferation of spinous cells in a papillary pattern; connective tissue is supportive stroma and not neoplastic
- Occasional papillomas show basilar hyperplasia and mild mitotic activity, often mistaken for mild epithelial dysplasia
- Koilocytes (HPV-altered epithelial cells with perinuclear clear spaces and nuclear pyknosis) may or may not be found in superficial epithelial layers
- Presence of chronic inflammatory cells may vary in the connective tissue
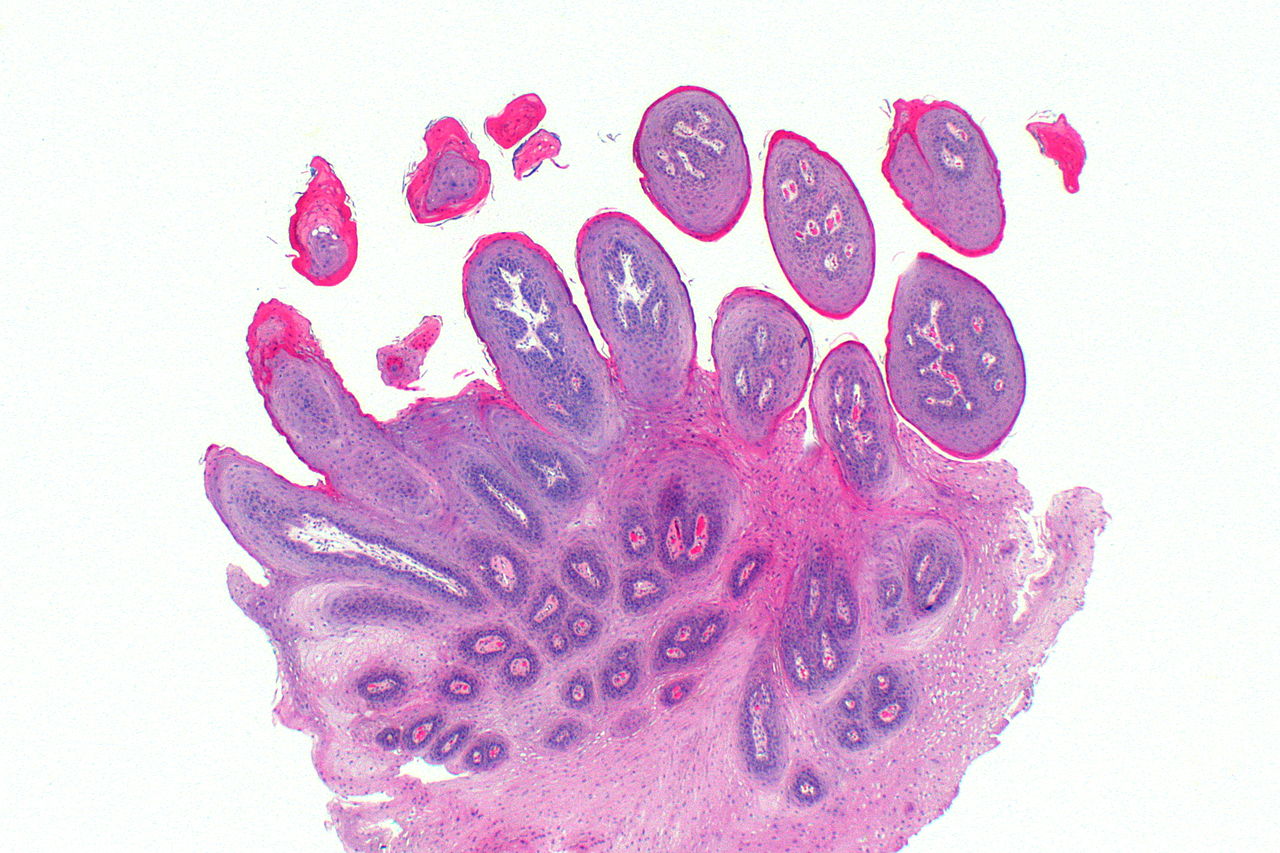
Squamous Papilloma Low Magnification
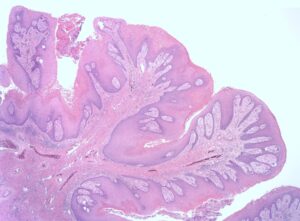
Squamous Papilloma High Magnification
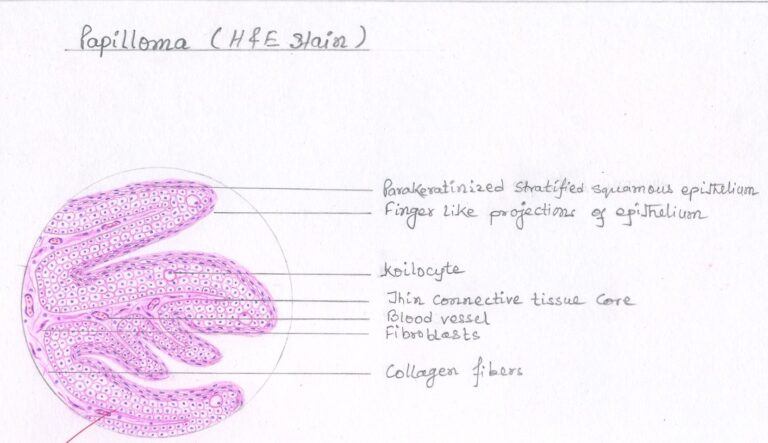
Squamous Papilloma – H & E Diagram
Treatment & Prognosis :-
- Excision involves removing the tumor, including the base of the mucosa where the pedicle or stalk inserts
- Proper excision typically results in rare recurrence of the tumor
References :-
- Shafer’s Textbook Of Oral Pathology
- Neville – Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology
- Image – Wikipedia & Wikimedia Commons


