Outline
- Lung abscess is defined as collection of pus in the lung parenchyma or there is a cavity lined by pyogenic membrane from where pus is expectorated into bronchus.
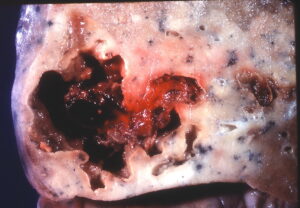
Causes
- Infectious Cause:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Klebsiella
- Anaerobes
- Mixed flora
- Actinomyces – These infections are acquired as a result of dental surgery, tonsillectomy, or other surgeries in the oral cavity
- Aspiration of fluids from GIT when patient is unconscious following GAs, patient with vocal cord palsies, reflux esophagitis
- Other Rare Causes:
- Pulmonary infarction
- Trauma
- Carcinoma lung or metastasis
- Amebic liver abscess
Symptoms & Signs
- Clinical Features:
- Localized pain at the site
- High fever with chills & rigors
- Pathognomonic Feature: cough with putrid foul-smelling sputum
- Rapid weight loss
- Clubbing
- On Examination:
- Abscess site is tender
- Stony dullness on percussion
- Loss of breath sound at abscess site
- Bronchial breath sound
- Increased Vocal Resonance
- Increased Tactile Vocal Fremitus
Investigation :-
- X-ray (PA
Chest):
- Lung abscess can be readily observed as a pus-filled cavity with fluid & air level.
- If the abscess cavity doesn’t contain air, it is difficult to distinguish from a tubercular mass or a tumor mass.
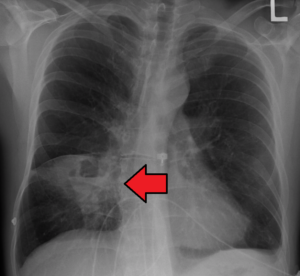
Lung Abscess on Chest X ray
- CT Scan:
- CT scan is performed when the diagnosis of a lung abscess is doubtful.
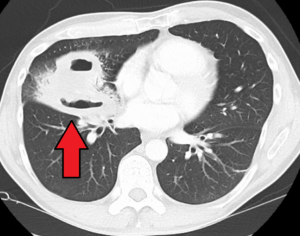
CT scan Lung Abscess
- Culture &
Sensitivity of Sputum:
- important to know the type of bacteria involved and antibiotics required
Management :-
- Improvement of General Health
- Postural Drainage of Pus
- The patient should tilt to the opposite side of the lung abscess for drainage.
- If postural drainage is ineffective, bronchoscopy may be needed for drainage.
- Specific Antibiotics (Based on Culture & Sensitivity) given for 10-14 days
- Physiotherapy
- Physiotherapy, including breathing exercises, is crucial for recovery.
List of important General Medicine questions – https://dentaledge.co.in/general-medicine-important-questions-for-dental-students/


